
2016-03-07 Dott.sa Carla Petta posted:
Fleas are insects of the order of the Sifonacteria, whose main characteristic is the adaptability to live on the pelami or on the feathers of warm-blooded animals.
The adults are equipped with sucker mouth piercing apparatus and use the hind limbs to jump and reach the host. The man's flea, Pulex irritans, can jump up to 19 cm vertically!
The eyes are very small or, in some species, literally absent, while the abdomen consists of segments provided with bristles turned in such a way as to facilitate movement in the host's pelage.
Unlike the adult flea that feeds on the host, the larvae almost always develop elsewhere, because the spawning almost always takes place in the nest or shelter of the host. Precisely for this reason, in the case of infestation on domestic animals, eggs and larvae proliferate in areas where the animals stay longer.
The ideal conditions for spawning have a temperature ranging between 18 ° and 27 ° with 70% humidity. The incubation period varies from 2 to 21 days.
The life cycle of the flea, in the various stages from egg to adult, lasts about 20 days. The nourishment of the larvae is mainly constituted by organic debris and excrement present in the host's lair and by blood droplets and excrements deposited by adult fleas. At the end of the larval cycle, the larva becomes pregnant in a cocoon: the duration in the pupa stage can vary from 7 days to almost a year.
Fleas are widespread in all continents and their presence in Sardinia is linked to the presence of a warm-blooded host.
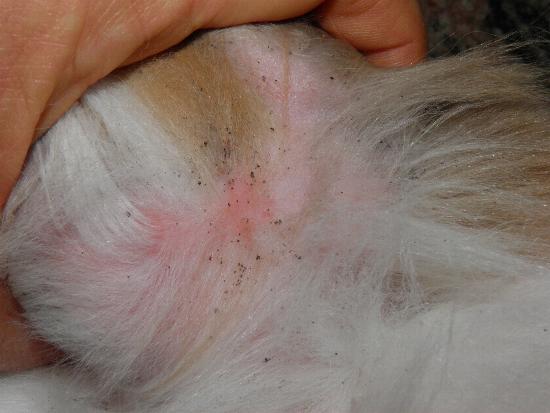
The ectoparasitic activity of fleas mainly causes infestations that can cause allergic dermatitis in response to saliva inoculations. Many species can transmit bacteria, viruses and rickettsias in wild and domestic hosts, especially in rodents. The transmission takes place both with the faeces that come into contact with the skin and with the bites.
Among the infectious diseases for humans transmitted by fleas we remember the bubonic plague, murine typhus and tularemia. Bubonic plague bacteria are acquired from the flea at the time of feeding on an infected host and cause intestinal blockage.
When the flea with this block tries to feed on another host, it regurgitates the bacteria in the wound, thus causing infection. Tularemia, on the other hand, is a bacterial disease transmitted to humans by rodent fleas by mechanical inoculation after an interrupted meal on an infected host.

Generally, compliance with the most common hygiene standards prevents human infestations, which however may occur due to the parasitic species of dogs and cats. In the daytime the fleas of pets stay in the cracks of the walls, skirting and parquet and in these cases you have to resort to the insecticide. If it is a heavy infestation, it is good to contact professionals.
The Gallura Disinfestazioni provides its experience to solve these types of infestations, very common in the territory of Sardinia.
Even pets should be treated, especially with powders and shampoos in the areas of the head, neck, perianal area and belly skin. These treatments must be repeated periodically as they have a very limited coverage period compared to a flea collar.